mfhowards
A matrix free implementation of policy iteration (a.k.a. Howard’s algorithm) in C++.
Description of Howard’s algorithm
Let C = C1 x C2 x … x Cn be a finite set. For each c = (c1, c2, …, cn) in C, let A(c) and b(c) be an n x n matrix and an n x 1 real vector (it is understood that the i-th rows of A(c) and b(c) depend only on ci).
Howard’s algorithm is used to find a vector v which satisfies the Bellman equation:
Remark: A sufficient condition for Howard’s algorithm to return the unique solution is for A(c) to be a monotone matrix for all c; see this paper or this one) for details and further results.
Boiler-plate code
Before trying to fill in the boiler-plate code below, I recommend also looking through the example.
#include <mfhowards>
#include <iostream>
using namespace mfhowards;
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Example with control set C = {eat, pray, code} x ... x {eat, pray, code}
// i.e., in each state, the controller can eat, pray, or code.
enum MyControlType { eat, pray, code };
// You are not restricted to using an enum for your control type!
// Any typename (e.g., double) works.
const auto A = [&](int i, int j, MyControlType c) {
// FILL THIS IN: Return the (i, j)-th entry of A(c)
return 0.;
};
const auto b = [&](int i, MyControlType c) {
// FILL THIS IN: Return the i-th entry of b(c)
return 0.;
};
auto results = howards_alg(
bellman_eq_from_lambdas<MyControlType>(
num_states, // Number of states
{ eat, pray, code }, // List of all controls
A, b // Matrix and vector
)
);
// Print results and return status
cout << results;
return results.status;
}
Example
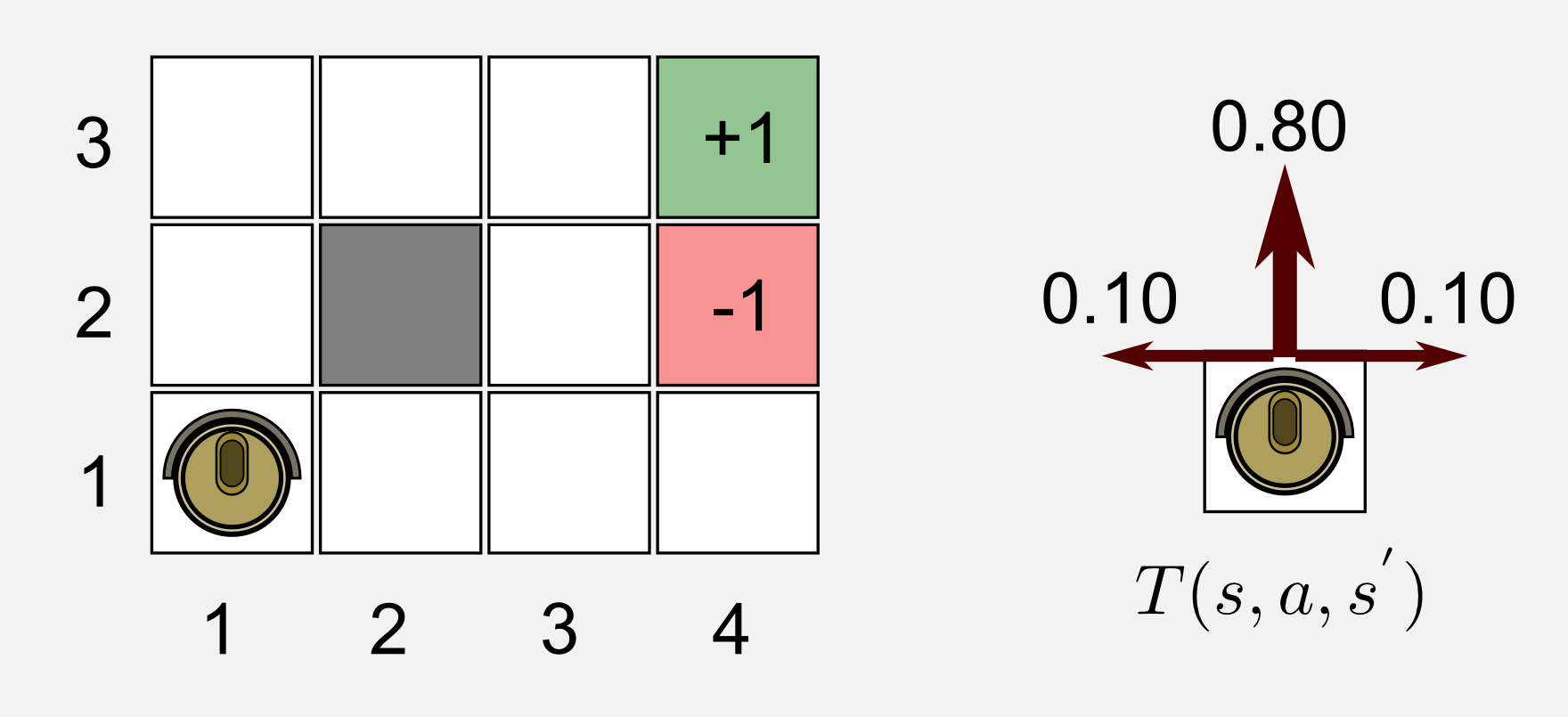
See examples/maze.cpp for an implementation of the robot navigation problem pictured above.
The problem is described in detail in
- a blog post by Massimiliano Patacchiola
- Chapter 17.1 of the Stuart and Norvig book
Advanced usage
The more general interface to the code is as follows:
template <typename Beq>
results howards_alg(Beq &&beq);
You can create your own Beq type to implement various methods called by howards_alg.
Some boiler-plate is given below:
class MyBeqType {
private:
MyMatrixType A_c;
MyVectorType b_c;
public:
/*
FILL THIS IN: This method should...
- Return the number of rows in A(c) and b(c).
*/
int rows() const;
/*
FILL THIS IN: This method should...
- Find a control c* = (c*_1, c*_2, ..., c*_rows()) minimizing A(c)x - b(c).
- Store A(c*) and b(c*) in A_c and b_c.
*/
void improve(const Eigen::VectorXd &x);
/*
FILL THIS IN: This method should...
- Solve the linear system A_c x = b_c.
- Return the solution x. The size of x should coincide with rows().
*/
Eigen::VectorXd rhs() const;
};